Science often deals with concepts that are difficult to understand, more or less abstract concepts for which not everyone is gifted to understand. The truth is that this is a mere excuse, it is not only necessary to know the concept and know how to explain it, that is what is truly difficult. In this article dedicated to density we will try to explain in a simple way what density is and what is its formula , types of densities , what are their units of measurement , etc. We will try to give examples that are easy to understand.
How to calculate density in chemistry
Density is symbolized by the letter rho (𝛒) of the Greek alphabet. We have said that it is the relationship between the mass and the volume of an object:
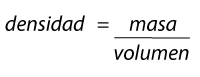
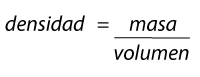
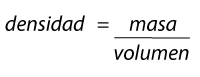
Formula density
Therefore the density formula is very simple:
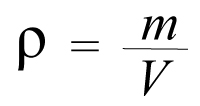
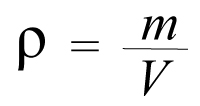
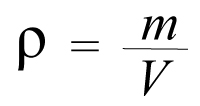
Where:
𝛒 = density
m = mass
V = volume
Density units
In the International System of Units , the most used units of measure are:
- kilogram per cubic meter (kg / m³) and its derivatives (g / cm³)
- kilogram per liter (kg / L) or per cubic decimeter (kg / dm³) and its derivatives (g / mL; g / cm³)
Summary;How is density calculated
To calculate the density it is necessary to use the following formula:
d = m / v
In this formula we have:
d = the density
m = the mass
v = the volume
Density is expressed in the International System (SI) as the unit of kilogram per cubic meter (kg/m 3 ). However, it is common for this quantity to be presented in grams per cubic centimeter (g/cm 3 ) or even in grams per milliliter (g/mL).
1 g / cm 3 = 1 g / mL = 1000 kg / m 3